- +91-9175557177
- admin@swarnatooltech.com
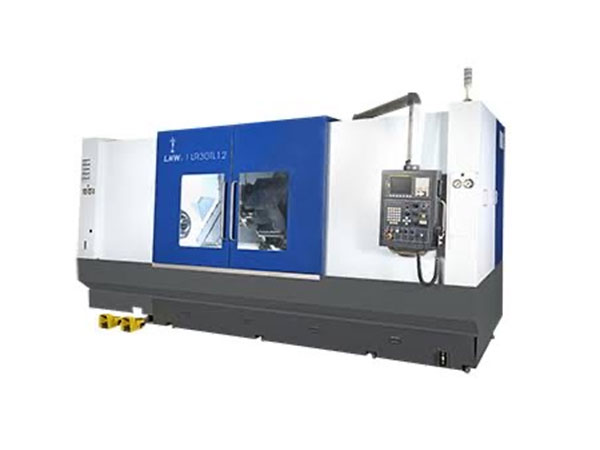

Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a manufacturing process in which pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. The process can be used to control a range of complex machinery, from grinders and lathes to mills and CNC routers.
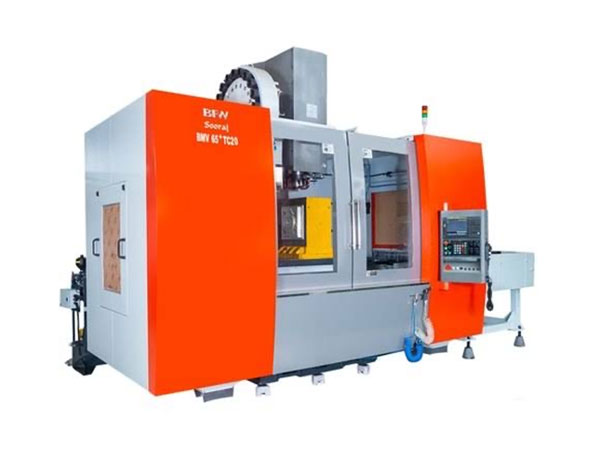

VMC machining refers to machining operations that utilize vertical machining centers (VMCs), which, as the name suggests, have vertically oriented machine tools. These machines are primarily utilized to turn raw blocks of metal, such as aluminum or steel, into machined components.
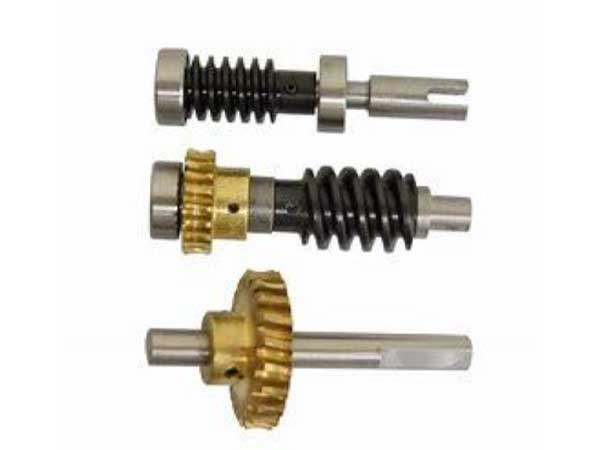

Sub-Assembly is the process that combines or builds components into component assemblies for inclusion in larger end items. It is the combining of components to create a new parent that requires assembly. This is a manufacturing process in and of itself.
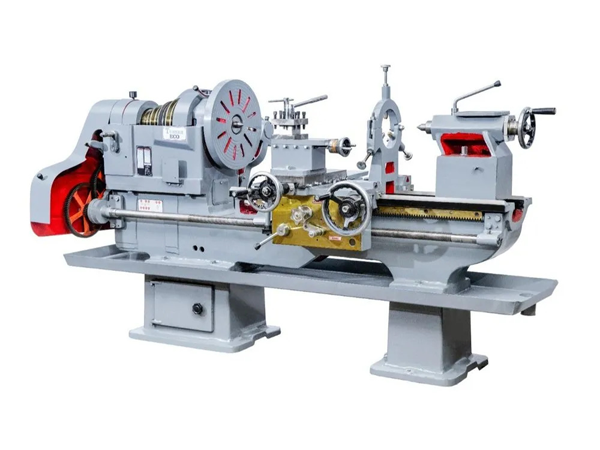
Turning is a machining process where a lathe is used to rotate the metal while a cutting tool moves in a linear motion to remove metal along the diameter, creating a cylindrical shape. The cutting tool can be angled differently to create different forms. It can be done manually or with a CNC turning machine.
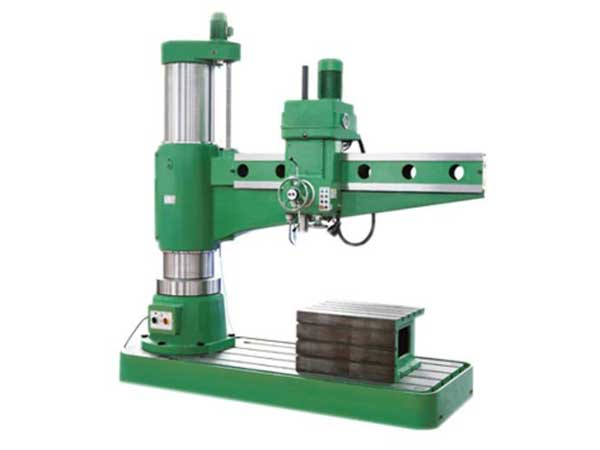

TAPPING is a machining process for producing internal threads. A tap is a cylindrical or conical thread-cutting tool having threads of a desired form on the periphery. Combining rotary motion with axial motion, the tap cuts or forms the internal thread.
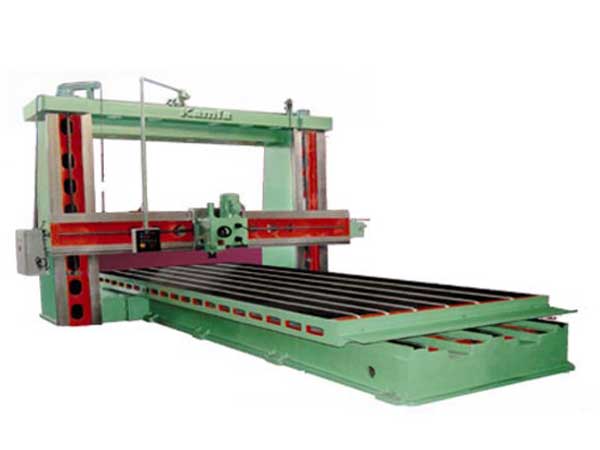

Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying direction on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure.